Retinal laser photocoagulation, sometimes referred to as focal laser, is a minimally invasive procedure performed in the office. Your physician may choose this option to treat leaking blood vessels in the retina due to disorders such as:
- Diabetic retinopathy
- Central serous retinopathy
- Macular edema
- Branch retinal vein occlusion
- Retinal microaneurysm
Retinal laser photocoagulation utilizes small, targeted laser burns on the retina in order to slow or stop the growth of the leaking blood vessels. Focal laser is utilized to treat a relatively small area of the retina with a limited amount of laser burns. The laser seals the leaking blood vessels in order to prevent, or slow vision loss. The main goal of retinal laser treatment is to ensure further vision loss is reduced, as well as to work to restore vision that has already been lost, although restoration may only be minimal.
Retinal laser is also used to treat retinal tears. When retinal laser photocoagulation is performed for a retinal tear, the laser is utilized to support the surrounding retina around the tear by creating a barrier of scar tissue ensuring that it stops the tear from progressing into a retinal detachment.
Multiple treatment options are available for the disorders listed above.
Each patient has individual needs and your physician will discuss all possible treatment options with you.
The retinal laser procedure is performed in the office. The eye of concern will be anesthetized, or numbed with topical eye drops prior to the procedure. The eye will also be dilated in order to allow the physician to view the retina as clearly as possible. A contact lens will be placed on the eye during the time of the procedure to magnify the vessels of concern. You will experience multiple bright light flashes, as the physician targets the leaking blood vessels with the laser. A technician will be by your side to provide support and assistance. For most patients, the treatment takes minutes to complete as the physician secures the problematic blood vessels. In some cases, multiple laser sessions may be required and your physician will review all options with you.
After the laser treatment is complete, your vision may appear darker than normal, blurry, and/or you may see spots. This is normal and your vision will be restored after a few minutes or within the next day.
Patients should have a family member or friend to drive them home as their pupils will be dilated for a few hours and they may be light-sensitive.
Retinal laser photocoagulation has a low risk of infection; however, patients may experience areas of decreased vision and reduced night vision. These effects may be temporary, but may last longer. The risk of severe, permanent loss of vision without treatment is greater than the mild side effects in vision post (after) laser treatment. Your physician will discuss the process with you and answer any of your questions.
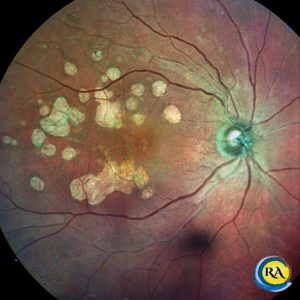
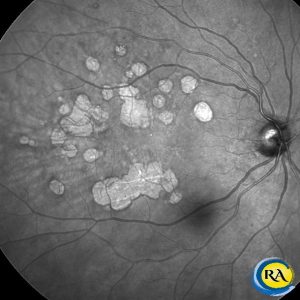
A multicolor image and an infrared image of a retina treated with focal retinal laser for leakage due to background diabetic retinopathy. The laser marks spare the central vision, thus maintaining optimal central vision.
